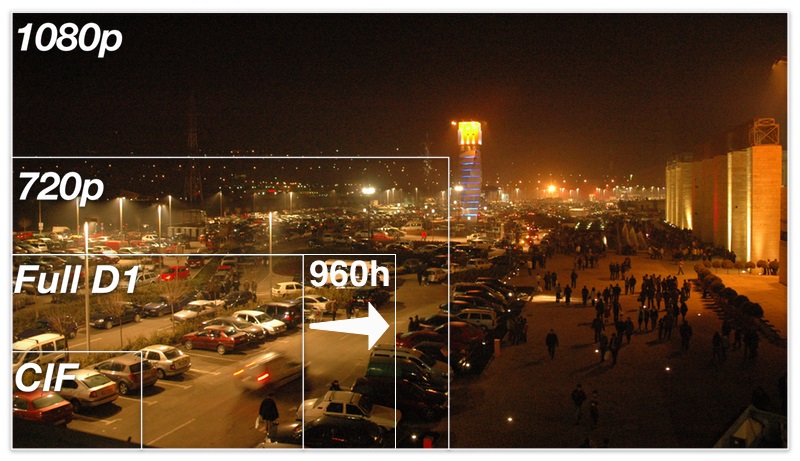
Videonovērošanas izšķirtspēju CIF / D1 / 960H / 720p / 1080p atšķīrība un salīdzināšana ar dažādiem standartiem.

Viens no būtiskākajiem, ja ne svarīgakajiem, punktiem veicot video ierakstus videonovērošanā ir IZŠĶIRTSPĒJA. Izšķirtspēju vispārīgi varam saukt par ieraksta kvalitāti. Tā ir atkarīga gan no kameras, gan no rakstītāja. No video ieraksta izšķirtspējas ir atkarīgs tas, cik ierakstītais video attēls ir dzidrs. Tā ir viena no būtiskākajām videonovērošanas iekārtas īpašībām, kas vienmēr ietekmē tās cenu. Izšķirtspēju mēra pēc horizontālajiem un vertikālajiem pikseļu daudzumiem attēlā un video ierakstā to ietekmē abi - gan kamera gan rakstītājs. Nebūs jēga iegādāties augstas izšķirtspējas kameru, ja DVR (video ieraksta iekārta) šo augstās izšķirtspējas video nespēj ierakstīt.
Tīri tehniski, lai saprastu, kas patiesībā ir izšķirtspēja un kāda ir tās nozīme praksē,
jāsāk ar vismazāko - attēla elementu, ko sauc par pikseli (px). Katrs
pikselis ekrānā vienlaicīgi var attēlot trīs krāsas RGB konfigurācijā
(sarkana, zaļa, zila) dažādās spilgtuma intensitātēs. Pateicoties tam,
iespējams attēlot katru krāsu.
Taisnstūra režģī simetriski
izvietota pikseļu kopa ir displejs.
Jo vairāk pikseļu ir attēlā, jo detalizētāks tas ir un jo augstāka izšķirtspēja.
Zemāk uzskaitītas mūsdienās videonovērošanā satopamās, populārākās izšķirtspējas:
ANALOGĀ VIDENOVĒROŠANA (nosaukums - izškirtspēja pikseļos (apraksts)):
- CIF - 352 x 240 (salīdzinoši - VHS ierakstu kvalitāte, mūsdienās novecojis standarts)
- D1 - 704 x 480 (DVD kvalitāte)
- 960H - 960 x 480 (platekrāna D1, mūsdienās augstākais iespējamais analogās videonovērošanas risinājums, DVD kvalitāte)
DIGITĀLĀS VIDEONOVĒROŠANAS standarti (nosaukums - izškirtspēja pikseļos (apraksts):
- HD-CVI, HD-TVI, AHD
Hibrīda analogās videonovērošanas standarti.
8Mpx (4K, UHD) - 4096 x 2304;
6MPx - 3072 x 2048;
5Mpx - 2592 x 1944; (5M-N - 1296 x 1944)
4Mpx - 2688 x 1520; (4M-N - 1280 x 1440)
3Mpx - 2048 x 1536;
2Mpx (zināms arī kā 1080p FullHD / 2MP - 1920 x 1080;
1Mpx (zināms arī kā 720p HD / 1.3MP) - 1280 x 720; - HD-SDI un EX-SDI
2mp (1080i) - 1920 x 1080;
8Mpx (4K, UHD) - 4096 x 2304; - IP tīkla kamerām pieejami visi iepriekšminētie izšķirtspēju standarti un mūsdienās nav ierobežojuma uz makimālo iespējamo izšķirtspēju. Viss atkarīgs no tehniskajiem resursiem.
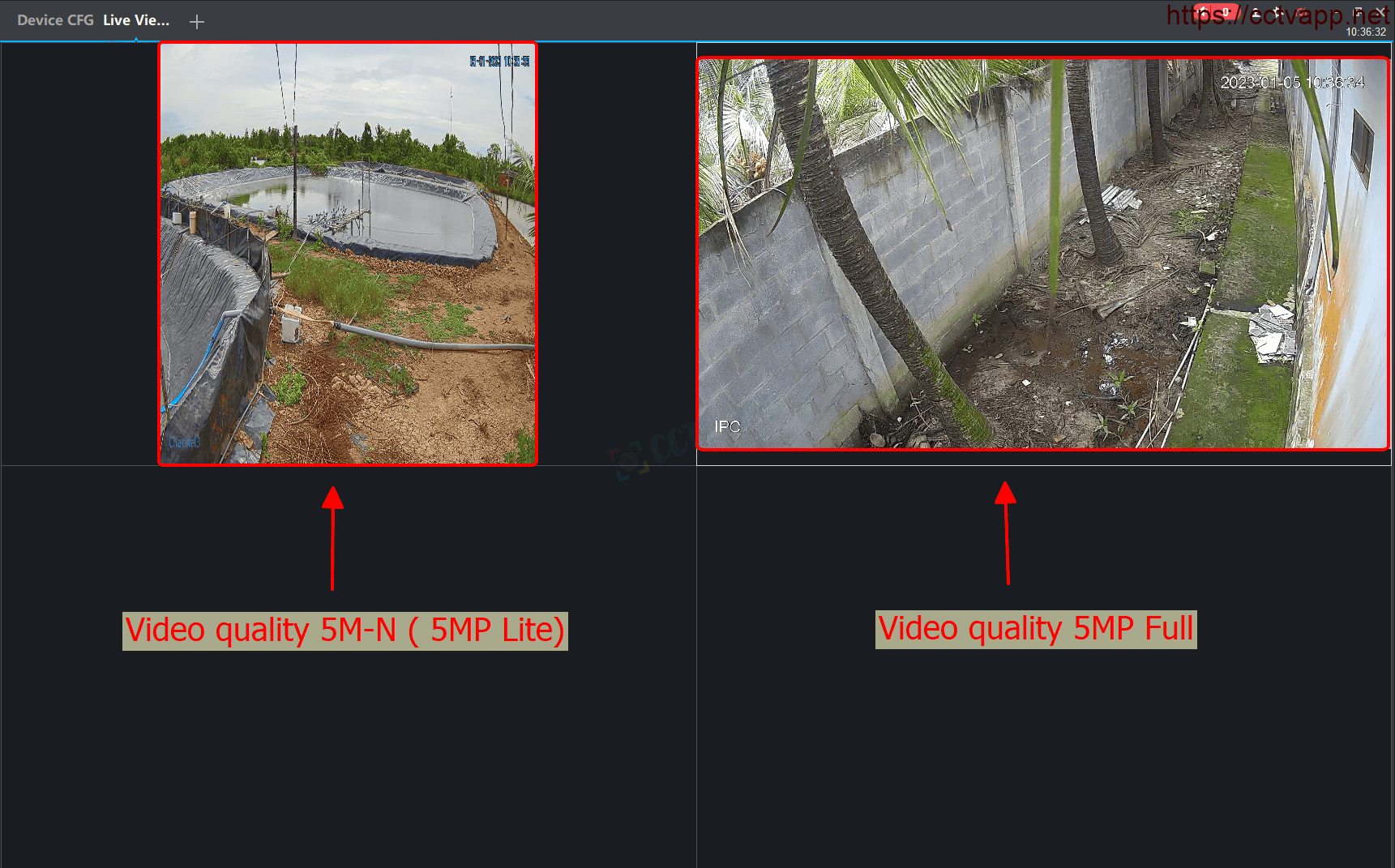
Ir sastopami rakstītāji, kas piedāvā veikt video ierakstītšanu ar kādu no iepriekšminētājām augstajām izšķirtspējām, taču klāt pievienots burts "N" vai "Lite", piemēram, "5M-N" vai 4M-Lite", šajā gadījumā netiks veikts pilnvērtīgs 5 vai 4 megapikseļu ieraksts. Rakstītājs sapratīs un spēs attēlot attiecīgās izšķirtspējas kameras raidīto attēlu, taču apstrādājot to, tas tik parādīts ar mazāku horizontālo pikseļu skaitu kā pie pilnas 5mp izšķirtspējas.
Praksē šāds apgriezsts izšķirtspējas risinājums samazina izmantoto ieraksta datu apjomu aptuveni par 30%, samazinās attēla detalizācija un zūd platekrāna malu attiecība (ņemiet vērā, ka tas neattiecas uz kameras redzamības leņķi - attēls drīzāk tiek iespiests kvadrātiņā).
Piemērs:
CIF izšķirtspēja (352 x 240)
CIF ir vissenākais, taču mūsdienās joprojām izmantots standarts. Izšķirtspēja pikseļos ir maza: 352 x 240. Kā pluss šādam standartam ir jāmin video ierakstu apjoms, jo dēļ mazās izšķirtspējas tas arī aizņem maz vietas video arhīvā. Šādas izšķirtspējas video ieraksts ir piemērots, ja nav nepieciešamība pēc detalizēta attēla. Piemēram, ja pietiek redzēt vai kāds piebraucis pie vārtiņiem, vai tie ir atvērti vai ciet, vai strādnieki strādā vai guļ utt.Šis pats standarts ir noderīgs arī, ja notiek attālināta pieslēgšanās no mobilajām ierīcēm, kur nozīmīgs ir internetā patērētais datu apjoms gan izmaksu ziņā, gan ātruma ziņā, tādēļ tas tiek izmantots arī IP kamerās, ka "Sub-stream" paralēla straumēšana ātrai piekļuvei pie kameras attēla, piemēram, no mobilajām ierīcēm. Mūsdienās kā norma ir sastopami DVR - video rakstītāji, kas nodrošinā CIF video ierakstu ar 25 kadriem/sekundē. Piemērotākās kameras šādam standartam ir analogās videonovērošanas kameras ar 420 - 480 līniju izšķirtspēju. Protams, var izmantot kameras ar augstāku (piemēram, 540, 600, 700, 800 utt.), taču video ierakstā šis labums pazudīs.
D1 izšķirtspēja (720 x 480)
D1 izšķirtspēja pikseļos ir 720 x 480. Mūsdienās viens no visplašāk izmantotajiem videonovērošanas ierakstu standartiem. Ierakstu ar D1 izšķirtspēju nodrošina gandrīz visi DVR, taču ne visi to spēj darīt ar 25k/s ((kadriem sekundē) (fps - frames per second)) katrai kamerai. Piemēram, ja 4 kanālu DVR spēj nodrošināt D1 ierakstu ar 100k/s, tad tas katrai kamerai būs 25k/s, taču, ja kopējais nodrošinātais kadru skaits ir 25k/s, tad katrai kamerai atliks vien 6.25k/s, kas vēlāk pārskatot video ierakstu liksies saraustīts.Pluss - mazākam kadru skaitam ir ietaupītais video arhīva apjoms.
Mīnuss - ātrāki objekti paliek ļoti saraustīti un atsevišķas lietas var palikt nepamanītas.
Piemērotākās kameras šādam standartam ir analogās videonovērošanas kameras sākot no 540 līniju izšķirtspējas (600, 700, 800tvl un vairāk).
960H izšķirtspēja (960 x 480)
960H izšķirtspēja pikseļos ir 960 x 480. Zināma arī kā WD1 (Widescreen D1 - platekrāna D1). Jaunākais un mūsdienās maksimālais iespējamais standarts analogājā videonovērošanā. Ne visi DVR video rakstītāji spēj ierakstīt video ar šo standartu un tie, kas spēj, ne visi to dara ar 25k/s katrai kamerai. Tieši tāpat kā ar D1 standartu. Piemēram, ja 4 kanālu DVR spēj nodrošināt D1 ierakstu ar 100k/s, tad tas katrai kamerai būs 25k/s, taču, ja kopējais nodrošinātais kadru skaits ir 25k/s, tad katrai kamerai atliks vien 6.25k/s, kas vēlāk pārskatot video ierakstu liksies saraustīts.Piemērotākās kameras šādam standartam ir analogās videonovērošanas kameras sākot no 540 līniju izšķirtspējas (600, 700, 800tvl un vairāk).
HD-CVI izškirtspēja (1280 x 720 (720p) un 1920 x 1080 (1080p))
HD-CVI ("high definition composite video interface" tulk. no angļu valodas - augstas izšķirtspējas kompozīta video interfeiss) standarts nodrošina divu veidu izšķirtspējas:720p (pikseļos = 1280 x 720), ko sauc arī par HD un
1080p (pikseļos = 1920 x 1080), ko sauc arī par FullHD.
HD-CVI standartam piemīt analogās video novērošanas īpašības (tiek izmantoti tie paši koaksiālie kabeļi, kas analogajā video novērošanā), taču tas vairs īsti nav analogs video. Kameras nodrošina attēlu, kas ir līdzvērtīgs 1.3MP un 2MP digitālajām IP kamerām!Arī šeit iegādājoties video ieraksta iekārtu DVR uzmanība jāpievērš ar kādu kadru skaitu sekundē rakstītājs spēj ierakstīt noteikto standartu. Piemēram, ja 4 kanālu DVR spēj nodrošināt 720p vai 1080p ierakstu ar 100k/s, tad tas katrai kamerai būs 25k/s, taču, ja kopējais nodrošinātais kadru skaits ir 25k/s, tad katrai kamerai atliks vien 6.25k/s, kas vēlāk pārskatot video ierakstu liksies saraustīts. Jāpievērš uzmanība, kāds kadru skaits ir atvēlēts katrai kamerai.
HD-SDI izšķirtspēja (1920 x 1080(1080p))
HD-SDI ("high-definition serial digital interface" tulk. no angļu valodas - augstas izšķirtspējas ciparu interfeiss) standarts nodrošina 1920 x 1080 pikseļu izšķirtspēju arī zināmu kā 1080p jeb FullHD.HD-SDI standartam piemīt analogās video novērošanas īpašības (tiek izmantoti tie paši koaksiālie kabeļi, kas analogajā video novērošanā), taču tas vairs īsti nav analogs video. Kameras nodrošina attēlu, kas ir līdzvērtīgs 2MP digitālajām IP kamerām!Piemērotākās kameras šādam standartam ir tikai un vienīgi HD-SDI kameras.+ Šis standarts ir piemērots, lai uzlabotu novecojušu analogās videonovērošanas sistēmu, izmantojot vecās sistēmas kabeļu instalācijas.
IP tīkla kameru izšķirtspēja no 0.3mp (640x480)
IP kameras nodrošina 1280 x 720 (720p), 1920 x 1080 (1080p) un pat 3mp (1536x2048) un 4mp (1704x2272) izšķirtspējas. Ir pieejami modeļi, kas nodrošina tikai 0.3MP (640x480), kas ir aptuveni līdzīgs D1 izšķirtspējai analogajā video. Atsevišķiem modeļiem ir iespējams uzstādīt vejadzīgo izšķirtspēju gan video straumēšanai gan ierakstam no 0.3mp līdz maksimālajam, ko kamera nodrošina.Apkopojot informāciju, zemāk redzams
attēls, kur iezīmētas robežas kaitras izšķirtspējas iespējām, kas
ilustrē atšķirību starp CIF, D1, 960H, 720p and 1080p izšīrtspējām.

